|
| Arduino Diecimila |
Overview
The Arduino Diecimila is a microcontroller board based on the
ATmega168 (
datasheet). It has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16
MHz
crystal oscillator, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and
a reset button. It contains everything needed to support the
microcontroller; simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or
power it with a AC-to-DC adapter or battery to get started.
"Diecimila" means 10,000 in Italian and was
named thusly to mark the fact that over 10,000 Arduino boards have been
made. The Diecimila is the latest in a series of USB Arduino boards.
Schematic & Reference Design
Note that R2 is not mounted and that R3 has been replaced by a 100 nano-farad capacitor.
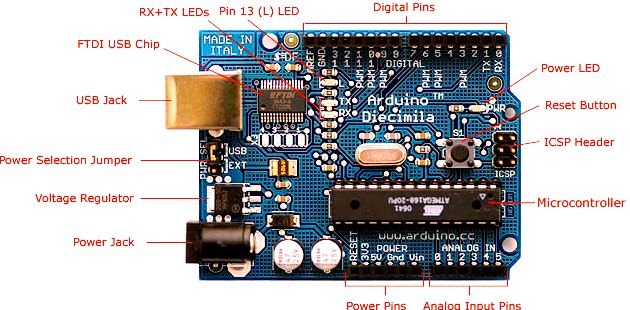 |
| Arduino Diecimila Parts, With Headings |
Power
The Arduino Diecimila can be powered via the USB connection or with
an external power supply. The power source is selected by the PWR_SEL
jumper: to power the board from the USB connection, place it on the two
pins closest to the USB connector, for an external power supply, the two
pins closest to the external power jack.
External (non-USB) power can come either from
an AC-to-DC adapter (wall-wart) or battery. The adapter can be
connected by plugging a 2.1mm center-positive plug into the board's
power jack. Leads from a battery can be inserted in the Gnd and Vin pin
headers of the POWER connector. A low dropout regulator provides
improved energy efficiency.
The board can operate on an external supply of 6
to 20 volts. If supplied with less than 7V, however, the 5V pin may
supply less than five volts and the board may be unstable. If using
more than 12V, the voltage regulator may overheat and damage the board.
The recommended range is 7 to 12 volts.
The power pins are as follows:
- VIN. The input voltage
to the Arduino board when it's using an external power source (as
opposed to 5 volts from the USB connection or other regulated power
source). You can supply voltage through this pin, or, if supplying
voltage via the power jack, access it through this pin.
- 5V. The regulated power
supply used to power the microcontroller and other components on the
board. This can come either from VIN via an on-board regulator, or be
supplied by USB or another regulated 5V supply.
- 3V3. A 3.3 volt supply generated by the on-board FTDI chip. Maximum current draw is 50 mA.
- GND. Ground pins.
Memory
The ATmega168 has 16 KB of flash memory
for storing code (of which 2 KB is used for the bootloader). It has 1
KB of SRAM and 512 bytes of EEPROM (which can be read and written with
the EEPROM library).
Input and Output
Each of the 14 digital pins on the Diecimila can be used as an input or output, using pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and digitalRead()
functions. They operate at 5 volts. Each pin can provide or receive a
maximum of 40 mA and has an internal pull-up resistor (disconnected by
default) of 20-50 kOhms. In addition, some pins have specialized
functions:
- Serial: 0 (RX) and 1 (TX).
Used to receive (RX) and transmit (TX) TTL serial data. These pins
are connected to the corresponding pins of the FTDI USB-to-TTL Serial
chip.
- External Interrupts: 2 and 3. These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge, or a change in value. See the attachInterrupt() function for details.
- PWM: 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, and 11. Provide 8-bit PWM output with the analogWrite() function.
- SPI: 10 (SS), 11 (MOSI), 12 (MISO), 13 (SCK).
These pins support SPI communication, which, although provided by the
underlying hardware, is not currently included in the Arduino language.
- LED: 13. There is a built-in LED connected to digital pin 13. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the pin is LOW, it's off.
The Diecimila has 6 analog inputs,
each of which provide 10 bits of resolution (i.e. 1024 different
values). By default they measure from ground to 5 volts, though is it
possible to change the upper end of their range using the AREF pin and
some low-level code. Additionally, some pins have specialized
functionality:
- I2C: 4 (SDA) and 5 (SCL). Support I2C (TWI) communication using the Wire library (documentation on the Wiring website).
There are a couple of other pins on the board:
- AREF. Reference voltage for the analog inputs. Used with analogReference().
- Reset. Bring this line
LOW to reset the microcontroller. Typically used to add a reset button
to shields which block the one on the board.
Communication
The Arduino Diecimila has a number of facilities for communicating
with a computer, another Arduino, or other microcontrollers. The
ATmega168 provides UART TTL (5V) serial communication, which is available on digital pins 0 (RX) and 1 (TX). An FTDI
FT232RL on the board channels this serial communication over USB and the
FTDI drivers
(included with the Arduino software) provide a virtual com port to
software on the computer. The Arduino software includes a serial
monitor which allows simple textual data to be sent to and from the
Arduino board. The RX and TX
LEDs on the
board will flash when data is being transmitted via the FTDI chip and
USB connection to the computer (but not for serial communication on pins
0 and 1).
A SoftwareSerial library allows for serial communication on any of the Diecimila's digital pins.
The
ATmega168 also supports
I2C (TWI) and SPI communication. The Arduino software includes a Wire library to simplify use of the
I2C bus; see the
documentation on the Wiring website for details. To use the SPI communication, please see the
ATmega168 datasheet.
Programming
The Arduino Diecimila can be programmed with the Arduino software (
download).
The
ATmega168 on the Arduino Diecimila comes preburned with a bootloader
that allows you to upload new code to it without the use of an external
hardware programmer. It communicates using the original
STK500 protocol (
reference,
C header files).
You can also bypass the bootloader and program the ATmega168 through the ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) header.
Automatic (Software) Reset
Rather then requiring a physical press of the reset button before an
upload, the Arduino Diecimila is designed in a way that allows it to be
reset by software running on a connected computer. One of the hardware
flow control lines (DTR) of the FT232RL is connected to the reset line of the ATmega168
via a 100 nanofarad capacitor. When this line is asserted (taken low),
the reset line drops long enough to reset the chip. Version 0009 of
the Arduino software uses this capability to allow you to upload code by
simply pressing the upload button in the Arduino environment. This
means that the bootloader can have a shorter timeout, as the lowering of
DTR can be well-coordinated with the start of the upload.
This setup has other implications. When the
Diecimila is connected to either a computer running Mac OS X or Linux,
it resets each time a connection is made to it from software (via USB).
For the following half-second or so, the bootloader is running on the
Diecimila. While it is programmed to ignore malformed data (i.e.
anything besides an upload of new code), it will intercept the first few
bytes of data sent to the board after a connection is opened. If a
sketch running on the board receives one-time configuration or other
data when it first starts, make sure that the software with which it
communicates waits a second after opening the connection and before
sending this data.
USB Overcurrent Protection
The Arduino Diecimila has a resettable polyfuse that protects your
computer's USB ports from shorts and overcurrent. Although most
computers provide their own internal protection, the fuse provides an
extra layer of protection. If more than 500 mA is applied to the USB
port, the fuse will automatically break the connection until the short
or overload is removed.
Physical Characteristics
The maximum length and width of the Diecimila PCB are 2.7 and 2.1
inches respectively, with the USB connector and power jack extending
beyond the former dimension. Three screw holes allow the board to be
attached to a surface or case. Note that the distance between digital
pins 7 and 8 is 160 mil (0.16"), not an even multiple of the 100 mil
spacing of the other pins.
Summary
| Microcontroller | ATmega168 |
| Operating Voltage | 5V |
| Input Voltage (recommended) | 7-12 V |
| Input Voltage (limits) | 6-20 V |
| Digital I/O Pins | 14 (of which 6 provide PWM output) |
| Analog Input Pins | 6 |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 40 mA |
| DC Current for 3.3V Pin | 50 mA |
| Flash Memory | 16 KB (of which 2 KB used by bootloader) |
| SRAM | 1 KB |
| EEPROM | 512 bytes |
| Clock Speed | 16 MHz |
Major Info. Source:- arduino.cc
Click Here to view information about all other official Arduino boards available in the market.